Bitumen Additives
Bitumen additives are substances that can be added to the bitumen binder to modify bitumen characteristics and thereby improve workability, the adhesion to aggregate, and the properties of the final asphalt mixture (Emulsifiers, Antistripping, CMA (Cold Mix Asphalt), Adhesion Improver,…)
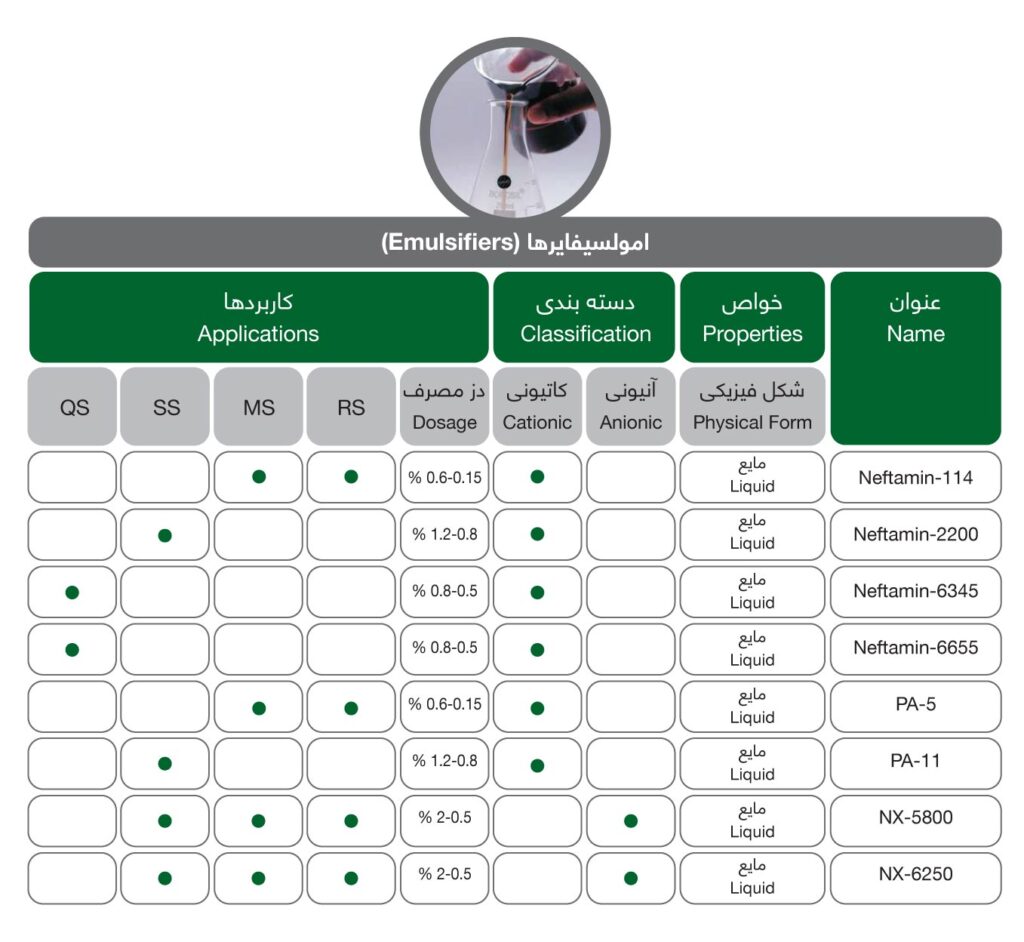
Emulsifier
An emulsifier is an amphiphilic molecule that is composed of a lipophilic tail (affinity for oil) and a hydrophilic head (affinity for water). This characteristic makes it possible to reduce the surface tension between two immiscible liquids such as oil and water. The use of an emulsifier and shear strength generates an oil-in-water or a water-in-oil dispersion.
Consequently, when bitumen and oil are mixed in the presence of an emulsifier, the shear strength of the colloid mill produces bitumen droplets into the water: a bitumen emulsion with stability controlled in time.
Emulsifiers perform several functions inside the bitumen emulsion:
- They facilitate emulsion production by reducing the interfacial tension between bitumen and water.
- They determine whether the emulsion is water-in-oil or oil-in-water.
- They stabilize the emulsion to prevent particle coagulation.
- They determine the emulsion’s functional properties, including breaking time and adhesion.
An emulsifier is the most important component of bitumen emulsions. For added effectiveness, the emulsifier should be water-soluble with a correct hydrophilic (attraction to water) and lipophilic balance (attraction to lipids (organic compounds that are water-insoluble but soluble in organic solvents and fats)). Emulsifiers are used separately or in mixtures to achieve specific properties.
Since the continuous phase of a bituminous emulsion is water, its viscosity is significantly lower than bitumen. This enables the handling of bituminous materials at ambient conditions in opposition to hot or warm techniques.
There are 3 categories of bitumen emulsifiers (as bitumen additives):
- Cationic: their hydrophilic head is positively charged.
- Anionic: their hydrophilic head is negatively charged.
- Amphoteric: their hydrophilic head is both positively and negatively charged. This way, they can perform either cationic emulsifiers or anionic emulsifiers depending on the pH.
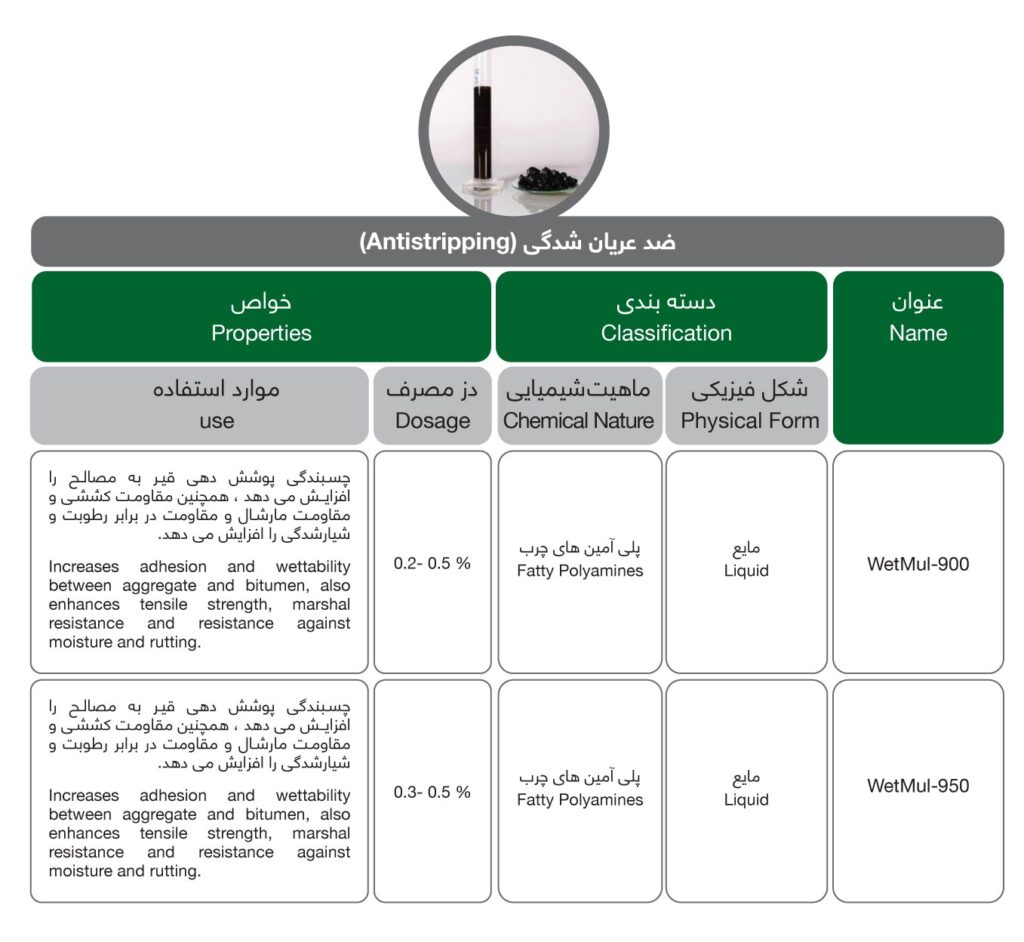
Anti-stripping
Antistripping is another kind of bitumen additives. Aggregates are naturally chemically more compatible with water than with bitumen. This is the reason why water propagates progressively at the interface between aggregates and bitumen, generating a stripping of bitumen vs. aggregates. Aggregates are then free and loose, and the life duration of the asphalt mix is significantly shortened.
Antistrippings increase adhesion and wettability between aggregate and bitumen, as well as increases tensile strength and marshal resistance, and resistance to moisture and rutting. This product is suitable for any new construction, maintenance, and maintenance of the upper, middle, and lower asphalt mixtures of the pavement.
Anti-stripping Features:
Asphalt anti-stripping agent is an advanced agent to improve the adhesion of petroleum and acid stone. It can achieve a better anti-stripping effect after adding 0.2-0.5% of the amount of asphalt and improve the adhesion level to 5, this product is suitable for acid stone and neutral stone, with strong adaptability, good compatibility with various asphalts, good thermal stability, good dispersion, good workability, environmental protection, safety, and aging resistance.
Performance:
- Ingredients: non-amine organic compounds;
- Appearance: brown-black-brown liquid;
- High-temperature resistance (use temperature greater than 300℃), good thermal stability;
- Solubility: good compatibility with various asphalt;
- Safety: environmental protection, safety, non-toxic, non-flammable, non-irritating odor, anti-aging;
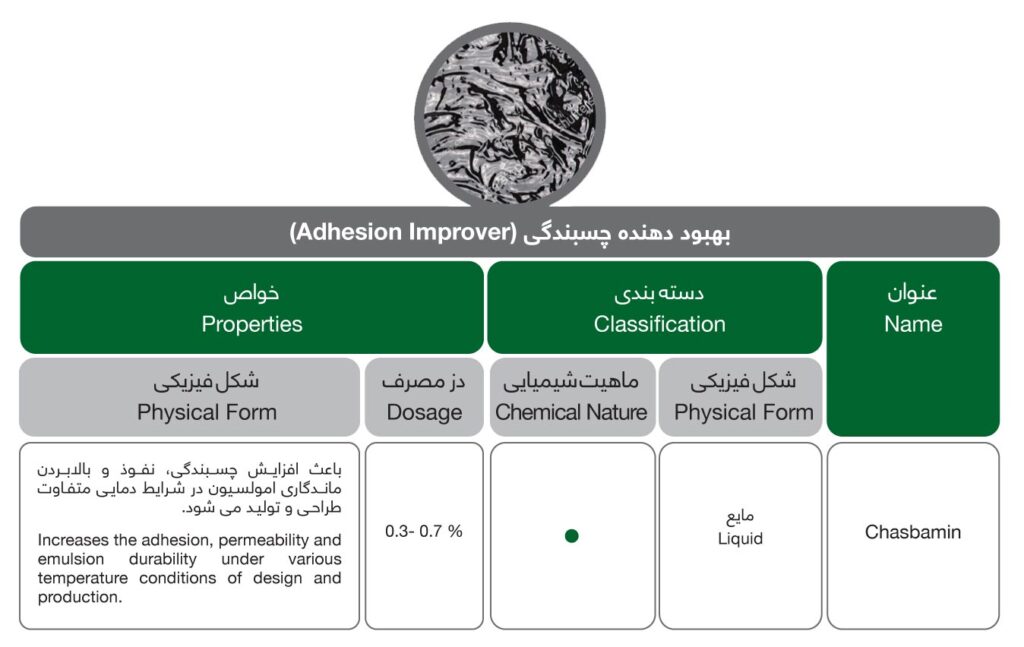
Adhesion Improver
(Bitumen Additives)
Adhesion Improver increases the emulsion’s adhesion, permeability, and durability under different temperature conditions of design and production. It is used in 0.5 – 1.5 % quantities relative to the bitumen depending on the type of bitumen and the kind of operation. The adhesion agent is mixed with the hot bitumen prior to mixing in the aggregate. Advantages of the use of adhesion agents are:
- more effective mixing and more straightforward application of the bitumen mix.
- the stripping of the top-bitumen layer from the bottom is prevented, especially when there is dew, mist, a rain shower, or in case the stones are wet.
- road making becomes less dependent on the weather and the conditions on-site.
- the effects of frost and the freezing and thawing at the binder/aggregate interface are largely eliminated.
The Adhesion Improver is used in:
- surface dressing: spraying a thin layer of hot bitumen, tar, or mixtures on the road surface, followed by the spreading of a layer of road stone.
- hot-mixing: using a hot mixture of bitumen, adhesion improver, and aggregate in constructing the base road.
- road-oiling: existing aggregates are stabilized with inexpensive heavy petroleum fractions (road oils).
The process can be applied to lightly trafficked roads in regions where winters are very cold and road surfaces are often subjected to frost damage.
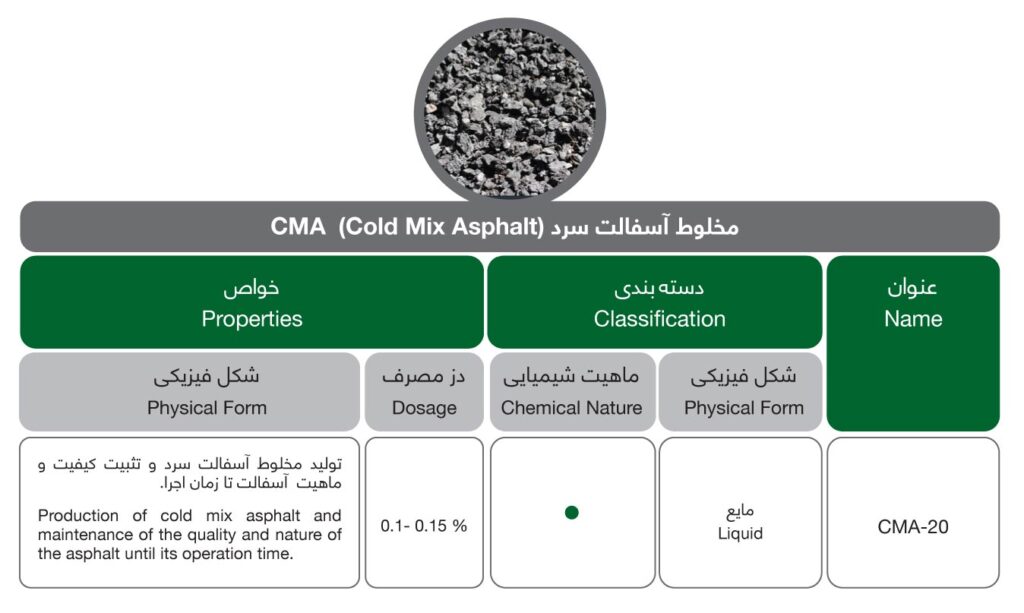
CMA (Cold Mix Asphalt)
(Bitumen Additives)
Cold Mix Asphalt (CMA) preserves the quality and nature of asphalt until its operation time. CMA is made of rock chip and polymer-modified asphalt, which keeps the asphalt soft without heating that is typically used for asphalt road and pothole repairs.
CMA does not require any heating of the material. This is achieved by using asphalt emulsion and cutback as binding material. Since these materials are liquid at room temperature, they do not require any heating for mixing and compaction. This gives many environmental and economic benefits to CMA over hot mix asphalt (HMA).